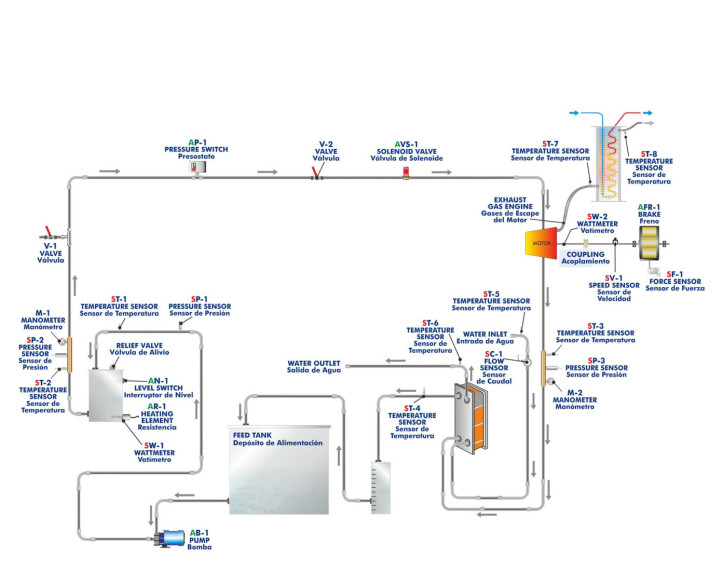
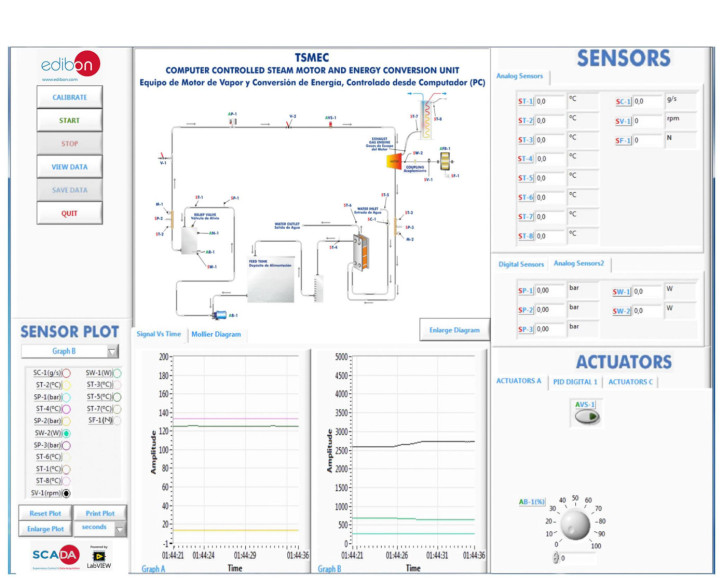
Thermodynamics and thermotechnology are fundamental fields of engineering that play a critical role across various industries, from energy generation to climate control. Understanding these foundational concepts is essential not only for engineers but also for fostering technological innovations...
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
We are excited to celebrate the publication of the article by Prof. Dr. Nina Penkova titled "Performance of Diffusion Absorption Refrigerators with Variable Input Power" The study explores how absorption refrigerators, which utilize waste or solar energy for heating and cooling, can operate...
 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences