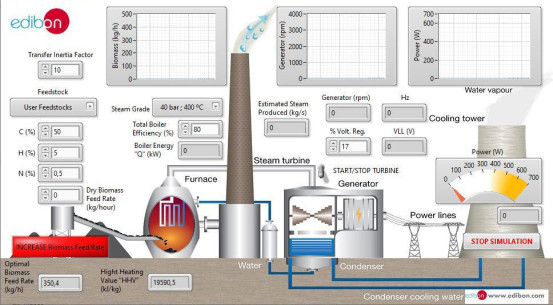
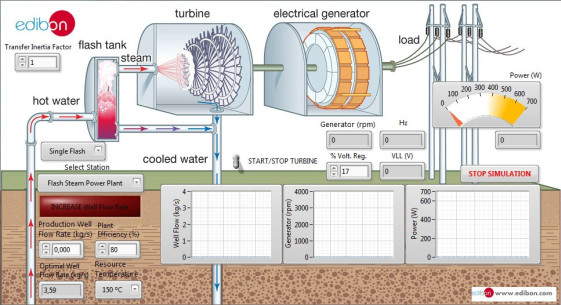
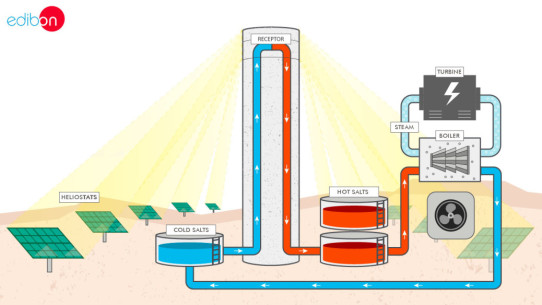
NEW Energy leaflet
With our complete Energy area, EDIBON gives answer to the academic demand for teaching and learning concepts of Energy, in an easy and practical way.
Read more
EDIBON and its commitment to European Skills
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also(...)
Read more
Recycling and energy storage systems
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has gained considerable momentum worldwide, promising a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a path to a more sustainable future. However, as the(...)
Read more
Laboratory supported by Official College of Technical Industrial Engineers (Spain)
At EDIBON, we reaffirm our commitment to the advancement of clean and renewable energy, with a special focus on green hydrogen as a key driver for a more sustainable future. We are proud to have(...)
Read more
Energy Storage: A key component of the energy future
The electrification of society and the ongoing expansion of renewable energy are profoundly transforming the global energy landscape. This transition to clean and sustainable sources presents a(...)
Read more
Microgrids: the future of decentralized energy explained with EDIBON’s AEL-MGP Equipment
For decades, the traditional energy model has relied on large, centralized power plants that generate electricity and distribute it through extensive grids to end users. While this model has(...)
Read more Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences