POAC Computer Controlled Advanced Oxidation Unit
INNOVATIVE SYSTEMS
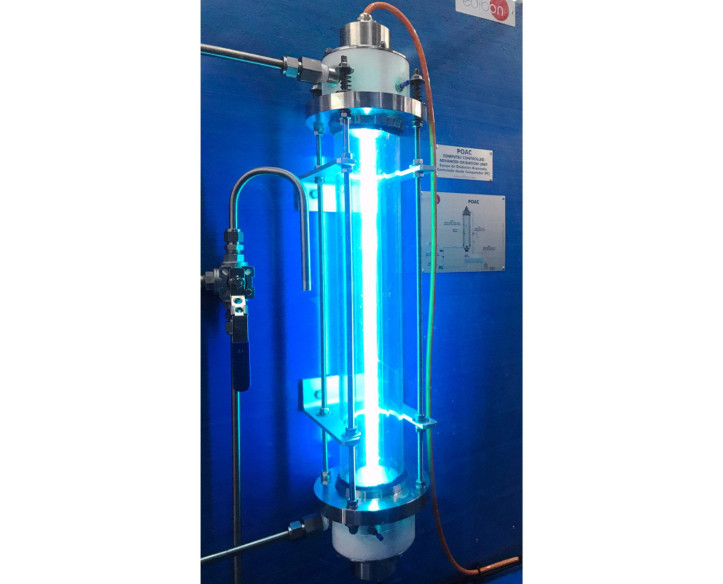
The Computer Controlled Advanced Oxidation Unit, "POAC", designed by EDIBON, allows to study advanced oxidation as a method to remove organic substances.
Expansions
Laboratories
RELATED NEWS
General Description
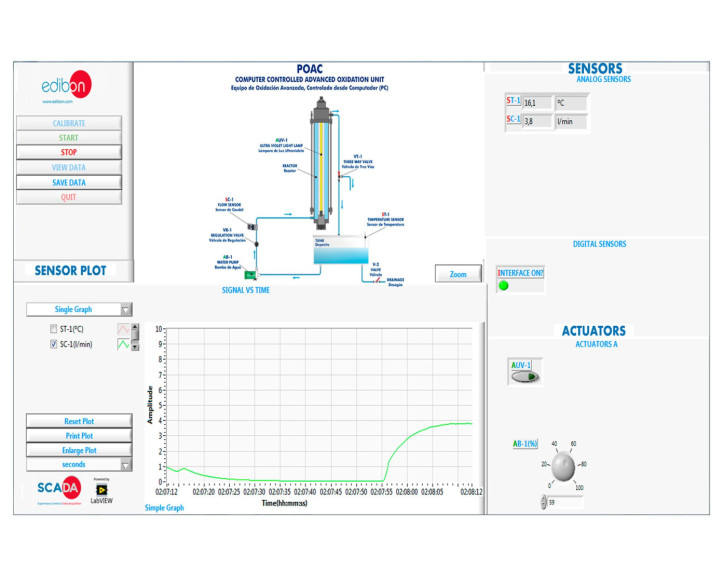
The Computer Controlled Advanced Oxidation Unit, "POAC", designed by EDIBON, generates hydroxyl radicals (OH-) through ultraviolet light radiation with hydrogen peroxide.
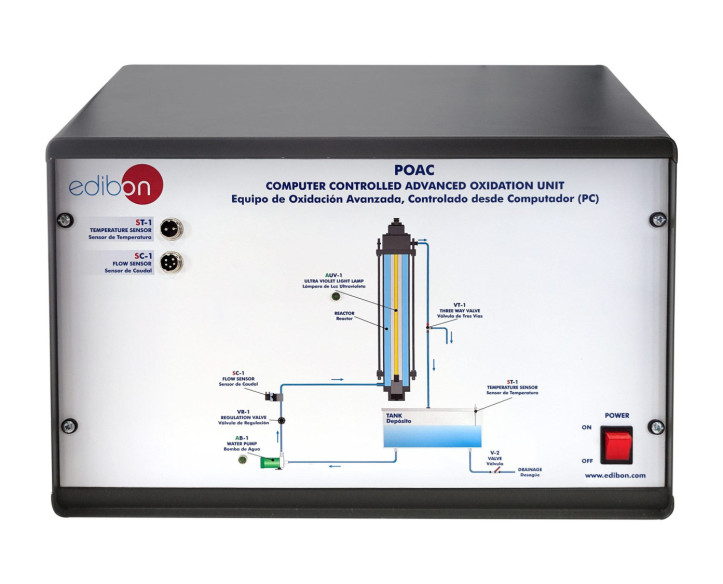
Raw water is enriched with hydrogen peroxide in a transparent tank and is driven by a computer controlled pump towards a reactor where an ultraviolet lamp with protective tube made of quartz is lodged.
The reactor has a manifold at its lower part that allows the flow of raw water forming a rising film on the inner walls of the reactor. As it ascends, it receives ultraviolet light radiation, forming hydroxyl radicals, which oxidize non-biodegradable soluble substances from the water to be treated.
The reactor is open by its lower side. Water flows towards the tank, forming a closed circuit. A flow sensor allows to measure the raw water flow rate through the circuit.
This Computer Controlled Unit is supplied with the EDIBON Computer Control System (SCADA), and includes: The unit itself + a Control Interface Box + a Data Acquisition Board + Computer Control, Data Acquisition and Data Management Software Packages, for controlling the process and all parameters involved in the process.
Exercises and guided practices
GUIDED PRACTICAL EXERCISES INCLUDED IN THE MANUAL
- Study of advanced oxidation process for wastewater treatment.
- Study of advanced oxidation with hydrogen peroxide and UV light.
- Influence of the amount of hydrogen peroxide in the oxidation process.
- Analysis of the reaction kinetics.
- Sensors calibration.
MORE PRACTICAL EXERCISES TO BE DONE WITH THE UNIT
- Many students view results simultaneously. To view all results in real time in the classroom by means of a projector or an electronic whiteboard.
- Open Control, Multicontrol and Real Time Control. This unit allows intrinsically and/or extrinsically to change the span, gains: proportional, integral, derivative parameters, etc. in real time.
- The Computer Control System with SCADA allows a real industrial simulation.
- This unit is totally safe as uses mechanical, electrical/electronic, and software safety devices.
- This unit can be used for doing applied research.
- This unit can be used for giving training courses to Industrieseven to other Technical Education Institutions.
- Control of the POAC unit process through the control interfacebox without the computer.
- Visualization of all the sensors values used in the POAC unitprocess.
- By using PLC-PI additional 19 more exercises can be done.
- Several other exercises can be done and designed by the user.
SUPPLEMENTARY EQUIPMENT
Computer Controlled and Touch Screen 1000 l Semicontinuous Centrifugal Separator
Computer Controlled Aerobic Digester
Aerobic Digester
Computer Controlled Anaerobic Digester
Anaerobic Digester
Computer Controlled Flocculation Test Unit
Flocculation Test Unit
Computer Controlled Aeration Unit
Aeration Unit
Computer Controlled Deep Bed Filter Unit
Deep Bed Filter Unit
Quality

AFTER-SALES SERVICE

 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences