For decades, the traditional energy model has relied on large, centralized power plants that generate electricity and distribute it through extensive grids to end users. While this model has proven effective, it now faces major challenges: the need to integrate intermittent renewable energy...
The electrification of society and the ongoing expansion of renewable energy are profoundly transforming the global energy landscape. This transition to clean and sustainable sources presents a critical challenge: how can we store energy efficiently, safely, and sustainably to ensure it is...
At EDIBON, we reaffirm our commitment to the advancement of clean and renewable energy, with a special focus on green hydrogen as a key driver for a more sustainable future. We are proud to have been selected to equip the first Green Hydrogen Laboratory in the Region of Murcia, a pioneering space...
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has gained considerable momentum worldwide, promising a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a path to a more sustainable future. However, as the demand for EVs accelerates, so too does the need for large quantities of essential minerals, such as...
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
The renewable energy engineering department of the @IsraUniversity.OfficialPage has fantastic students and that is why we are very proud and happy about our installation. The equipment that they can now enjoy to continue training are the Wind Energy UnitEquipos, EEE, the Kit of Conversion and...
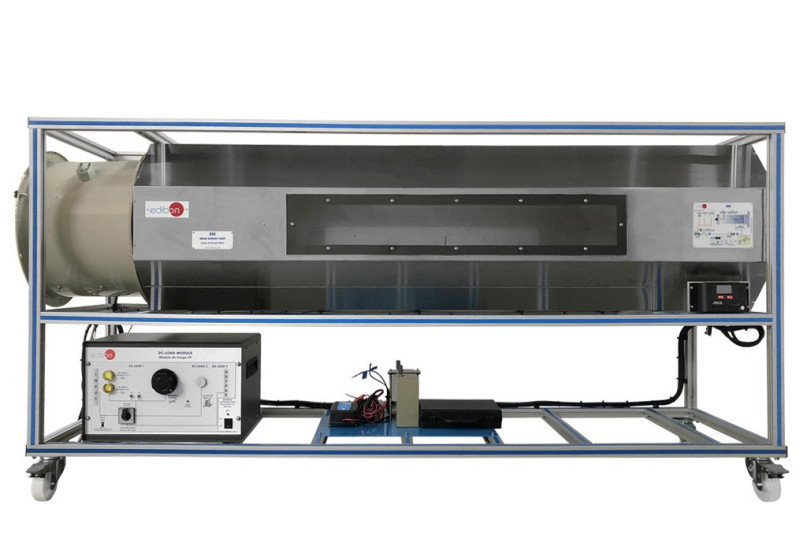
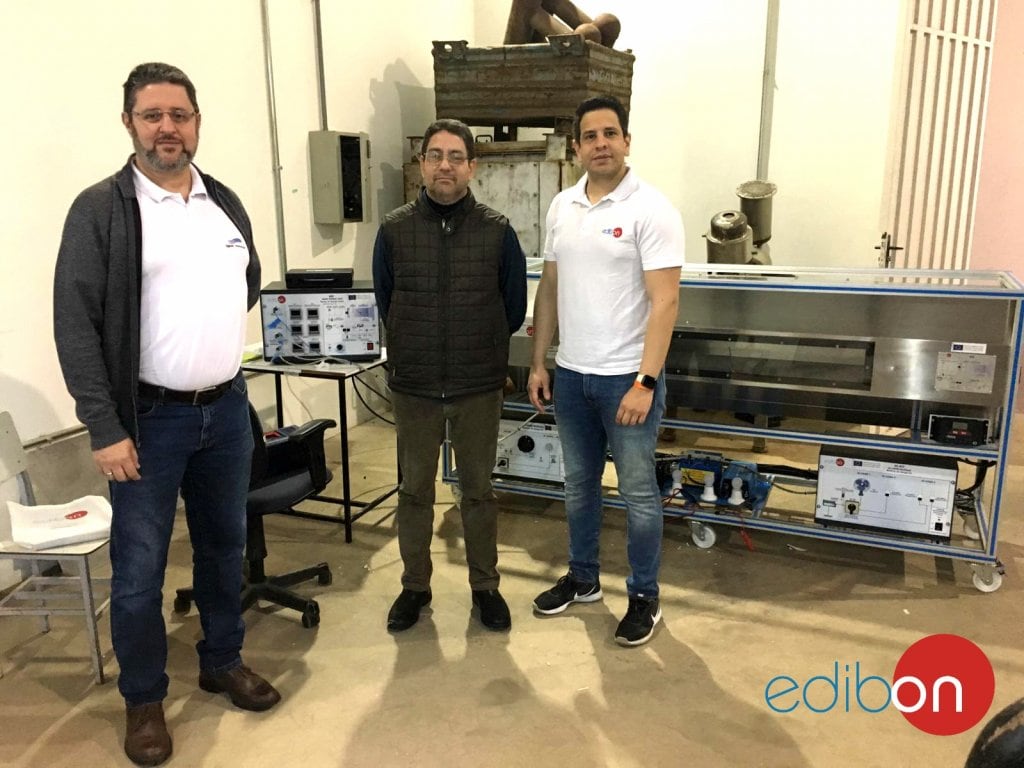
We are very happy to have participated in the installation of the wind energy unit (EEE) at Unifei - Universidade Federal de Itajubá . Now both professors and students will be able to continue researching and learning about renewable energy, a topic that is becoming increasingly important and...
Are you a teacher or do you work as an engineering researcher? EDIBON offers courses for teachers and #research staff. Take a look at the course of Fluid Mechanics and learn about #fluids properties. #DiscoverEdibon #Engineering.
 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences