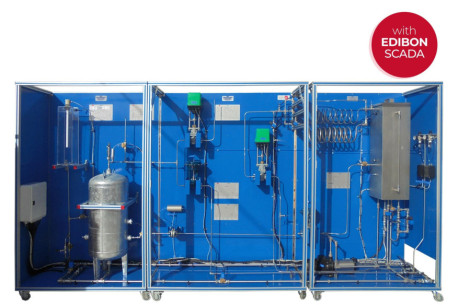
NEW Process Control leaflet
With our complete Process Control area, EDIBON gives answer to the academic demand for teaching and learning concepts of Process Control, in an easy and practical way.
Read more
Completion of the Course of Instrumentation, Regulation and Control in Laboratories
On October 19th, the Course on Instrumentation, Regulation and Control in Laboratories, taught by our engineers in these facilities, using EDIBON units, was completed and aimed at learning the(...)
Read more
EDIBON and its commitment to European Skills
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also(...)
Read more
What is Process Control, and Why is It Essential in Modern Industry?
Today, automation and efficiency are key factors in industrial and scientific development. Process control plays a crucial role in this context by enabling the monitoring, regulation, and(...)
Read more
The future of Process Control: Innovation, training, and the industry 4.0 revolution
Automation and process control have been fundamental pillars in the evolution of both industry and scientific research. With the advent of Industry 4.0, the integration of new technologies has(...)
Read more Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences