TIVAC Computer Controlled Steam to Water Heat Exchanger
INNOVATIVE SYSTEMS
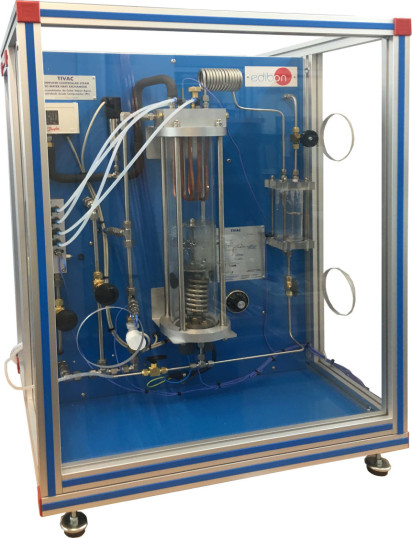
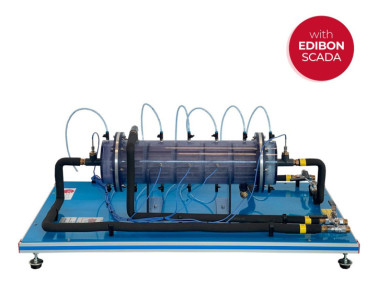
The Computer Controlled Steam to Water Heat Exchanger, "TIVAC", is a unit designed to study condensation phenomena in shell and tube heat exchangers.
Expansions
Laboratories
RELATED NEWS
General Description
The Computer Controlled Steam to Water Heat Exchanger, "TIVAC", is a unit designed to study condensation phenomena in shell and tube heat exchangers.
It mainly consists of a steam chamber, which is a vertical cylinder made of resistant glass. The helical heating element is located at the bottom. It provides heat to a given volume of water contained in the chamber.
The condenser is located at the upper side of the chamber. It is formed by a group of four U-shape copper tubes arranged in series. The way of configuring the condenser in one, two, three or four passes is easily changed with manual valves.
The cooling fluid (tap water) that will be heated in the condensation process passes through this system of tubes of the condenser. For a constant cooling water flow, the heat transfer surface will increase as the number of passes in the condenser increases.
The steam generated in the chamber by the heating element rises towards the tubes of the condenser, where it is condensed on the external surface of those tubes. Once condensed, it drops to the bottom of the steam chamber, where it is evaporated again.
The unit includes a vacuum system (water jet pump) to boost the evaporation. This system makes it possible to reach a negative pressure in the steam chamber, decreasing the water boiling temperature. Likewise, this system assists the process by extracting the air initially contained in the chamber, so that there will be only water and steam in the chamber.
This Computer Controlled Unit is supplied with the EDIBON Computer Control System (SCADA), and includes: The unit itself + a Control Interface Box + a Data Acquisition Board + Computer Control, Data Acquisition and Data Management Software Packages, for controlling the process and all parameters involved in the process.
Exercises and guided practices
GUIDED PRACTICAL EXERCISES INCLUDED IN THE MANUAL
- Demonstration of dripping condensation, film condensation and nucleate boiling phenomenon.
- Influence of the number of passes on heat transfer.
- Influence of the heat transfer area in the overall heat transfer coefficient (U).
- Influence of the pressure drop on the overall heat transfer coefficient (U).
- Demonstration of the pressure drop with the number of passes.
- Study of the heat transfer efficiency.
- Study of the saturation pressure and temperature of the water at low pressures.
MORE PRACTICAL EXERCISES TO BE DONE WITH THE UNIT
Additional practical possibilities:
- Global balance of energy in the exchanger.
- Infuence of the cooling fluid flow in the overall heat transfer coefficient (U).
- Infuence of the steam chamber air effect on the overall heat transfer coefficient (U).
- Demonstration of the Venturi effect.
Other possibilities to be done with this Unit:
- Many students view results simultaneously.
- To view all results in real time in the classroom by means of a projector or an electronic whiteboard.
- Open Control, Multicontrol and Real Time Control.
- This unit allows intrinsically and/or extrinsically to change the span, gains, proportional, integral, derivative parameters, etc, in real time.
- The Computer Control System with SCADA and PID Control allow a real industrial simulation.
- This unit is totally safe as uses mechanical, electrical and electronic, and software safety devices.
- This unit can be used for doing applied research.
- This unit can be used for giving training courses to Industries even to other Technical Education Institutions.
- Control of the TIVAC unit process through the control interface box without the computer.
- Visualization of all the sensors values used in the TIVAC unit process.
- By using PLC-PI additional 19 more exercises can be done.
- Several other exercises can be done and designed by the user.
SUPPLEMENTARY EQUIPMENT
Base Service Unit (Common for all available Heat Exchangers type "TI")
Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger for TICC
Extended Concentric Tube Heat Exchanger for TICC
Plate Heat Exchanger for TICC
Extended Plate Heat Exchanger for TICC
Shell & Tube Heat Exchanger for TICC
Jacketed Vessel Heat Exchanger for TICC
Coil Vessel Heat Exchanger for TICC
Turbulent Flow Heat Exchanger for TICC
Cross Flow Heat Exchanger for TICC
Heat exchanger Training System
Quality

AFTER-SALES SERVICE

 Cookie preferences
Cookie preferences