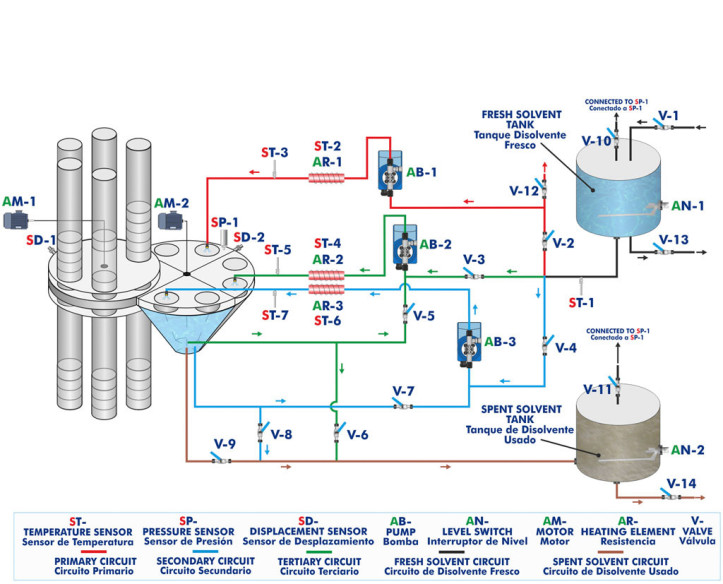
The Computer Controlled and Touch Screen Solid-Liquid Extraction Pilot Plant, "SLE00", allows the separation of a solute from its solid matrix by direct contact with a suitable solvent.
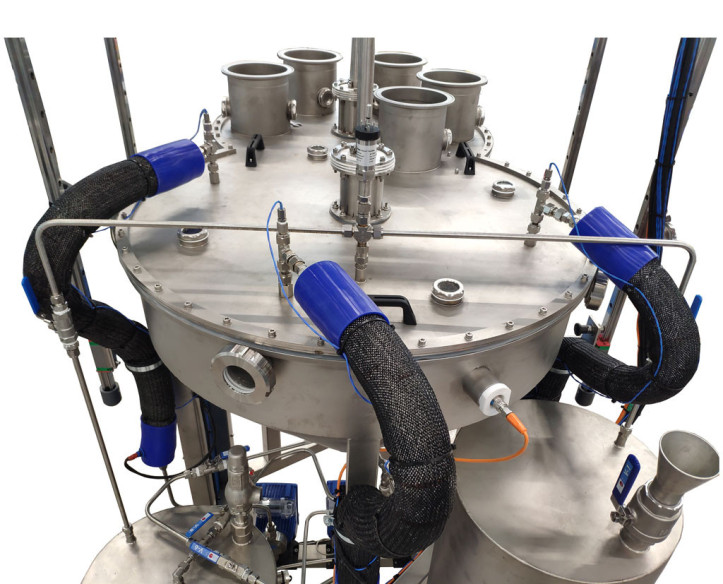
The pilot plant incorporates five columns that can store up to 18 vessels of about 200 ml capacity, which allows loading up to 15 – 18 liters of solids. The PTFE and stainless steel vessels are loaded with the solid prior to the operation, and then the columns are filled by stacking the vessels on top of each other.
Once the pilot plant has been preloaded and correctly assembled, the servomotors that drive the different carousels are started. The feeding carousel doses the sieves into the extraction zone, one by one.
In the extraction zone, the solid from each sieve undergoes six different stages, with three consecutive extraction and draining cycles.
After each extraction stage there is a resting stage that allows the solvent to drain, optimizing the recovery of the solute. This pilot plant allows for a countercurrent solid-liquid extraction process, which is the most commonly used in the industry because it is the most efficient. The solid is depleted from the first to the last stage, while the solvent is concentrated in solute from the last to the first stage.
When the extraction stage is finished, the depleted solid passes to the emptying carousel, where the vessels are dosed into five columns similar to the feed columns. The sieves fall into these columns by gravity and will remain there until the process is finished.
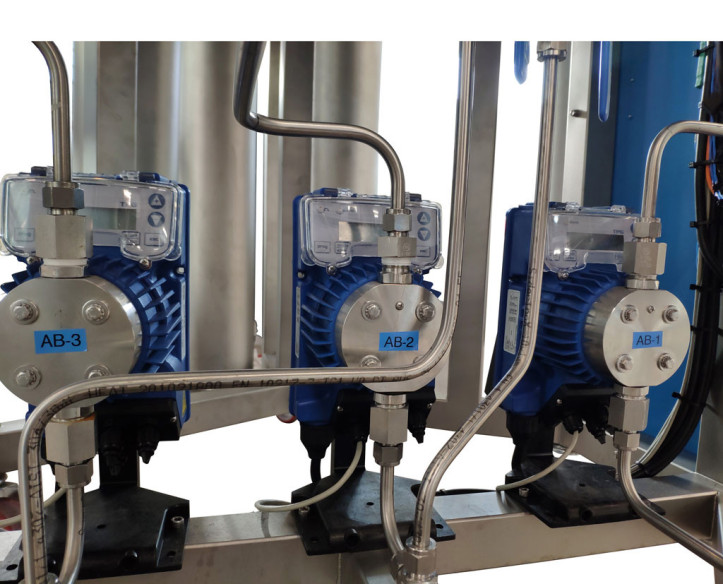
The liquid used as solvent for the extraction starts from the storage tank or fresh solvent tank. This solvent is pumped by a dosing pump to the last stage of extraction of the solid (which corresponds to the first stage of solvent extraction), the solvent passes through a heating hose that raises the temperature of the liquid and is injected into the container with the solid through a spray nozzle. The bottom of the vessels on which the solid is placed is made of stainless steel mesh which allows the solvent together with the solute to pass through, but retains the solid material. The solvent is collected at the bottom of the unit body in a compartment with an outlet leading to another dosing pump, the solvent is reheated and fed to the second extraction stage. The same process then takes place until the solvent is fed to the first extraction stage.
When the solvent from the first extraction stage is collected (from the point of view of the solid) it is completely exhausted, having the maximum concentration of solute, therefore, it is led to the spent solvent storage tank.
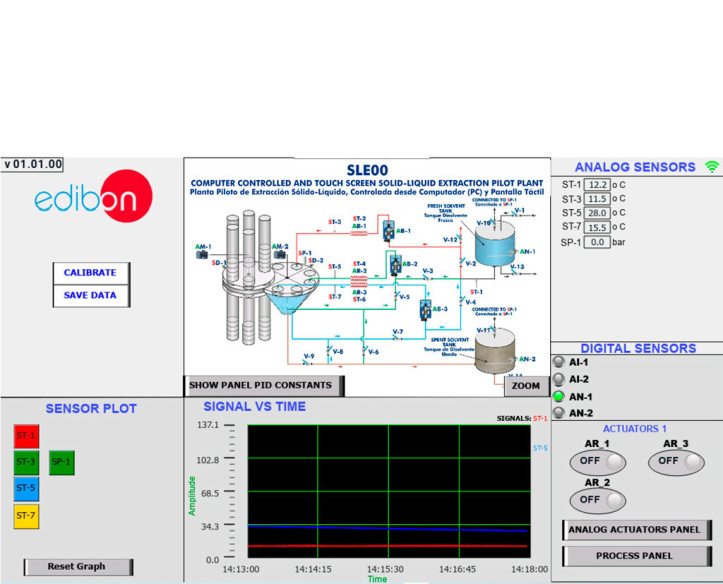
This computer controlled unit is supplied with the EDIBON Control System (SCADA), and includes: The unit itself + Control, Data Acquisition and Data Management Software Packages, for controlling the process and all parameters involved in the process.
 クッキーの設定
クッキーの設定