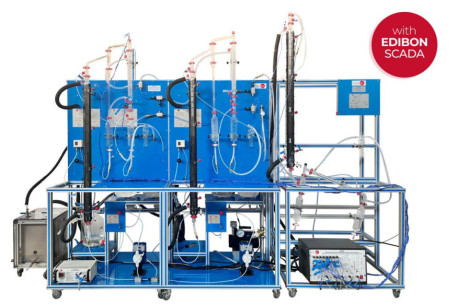
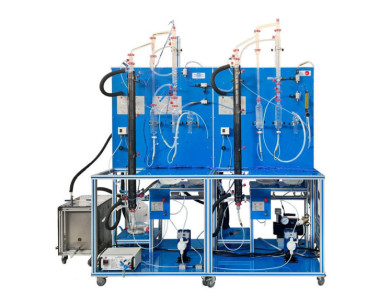
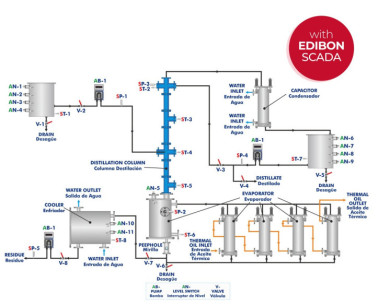
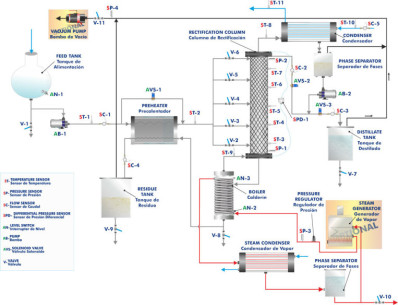
NEW Chemical Engineering leaflet
With our complete Chemical Engineering area, EDIBON gives answer to the academic demand for teaching and learning concepts of Chemical Engineering, in an easy and practical way.
Lesen Sie mehr
Second-generation biofuels: the sustainable future at EDIBON
In a world where energy demand continues to rise and non-renewable resources are rapidly depleting, the need for sustainable, environmentally friendly solutions has never been more urgent. The(...)
Lesen Sie mehr
EDIBON and its commitment to European Skills
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also(...)
Lesen Sie mehr
ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition 2025
Once again, EDIBON had the honor of participating in one of the most significant international events in the field of engineering education: the ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition 2025,(...)
Lesen Sie mehr Cookie-Präferenzen
Cookie-Präferenzen