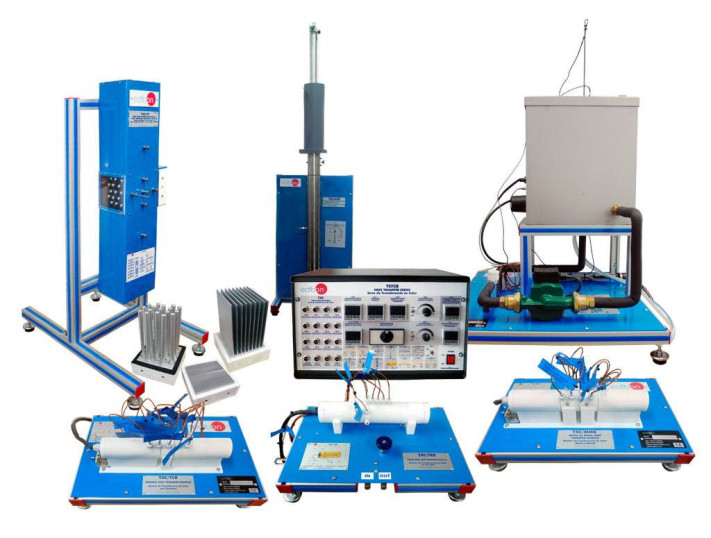
РУКОВОДСТВО ПО ПРАКТИЧЕСКИМ УПРАЖНЕНИЯМ ВКЛЮЧЕНО В РУКОВОДСТВО ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЯ
Practices to be done with the Linear Heat Conduction Unit for TSTCB (TXC/CLB):
- Conduction through a simple bar.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity "k".
- Conduction through a compound bar.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity, k, of the stainless steel.
- Determination of the thermal contact resistance Rtc.
- Effect of the cross sectional area.
- Insulating effect.
Additional practical possibilities:
- The thermal conductivity properties of insulators may be found by inserting paper or other elements between the heating and cooling sections.
- Understanding the use of the Fourier equation in determining rate of heat flow through solid materials.
Practices to be done with the Radial Heat Conduction Unit for TSTCB (TXC/CRB):
- Radial conduction: Dependence on heating power.
- Radial conduction: Dependence on refrigeration flow.
Additional practical possibilities:
- Radial conduction.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity "k".
- Determination of the thermal contact resistance Rtc.
- Insulation effect.
- Understanding the use of the Fourier equation in determining rate of heat flow through solid materials.
Practices to be done with the Radiation Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/RCB):
- Inverse of the distant square law for the radiation.
- Stefan Boltzmann Law.
- Emission power I.
- Emission power II.
- Kirchorff Law.
- Area factors.
- Inverse of the distant square law for the light.
- Lambert´s Cosine Law.
- Lambert Law of Absorption.
Practices to be done with the Combined Free and Forced Convection and Radiation Unit for TSTCB (TXC/CCB):
- Demonstration of the combined heat transfer effect by radiation and convection on the surface of the cylinder. Determination of the combined heat transfer effect by forced convection and radiation.
- Demonstration of the influence of air flow in the heat transfer. Determination of the combined heat transfer effect by forced convection and radiation.
- Demonstration of the influence of input power in the heat transfer. Determination of the combined heat transfer effect by forced convection and radiation.
- Demonstration of the combined heat transfer effect of the radiation and convection on the surface of the cylinder. Determination of the combined heat transfer effect by free convection and radiation.
- Determination of the airflow.
Practices to be done with the Radiation Errors in Temperature Measurement Unit for TSTCB (TXC/ERB):
- Measurement the errors in thermocouples in function of its painting, material of its capsules, size.
- Radiation errors in temperature measurement and minimization of radiation errors due to shielding.
- Influence of the air flow on radiation errors in temperature measurement.
Additional practical possibilities:
- Heat transfer from geometry.
- Effect of cross-sectional shape on heat transfer from a geometry.
- Heat transfer from geometries of two different materials.
- Radiation errors in temperature measurements.
- Effect of air velocity on measurement errors.
Practices to be done with the Extended Surface Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/SEB):
- Heat transfer from a Fin.
- Effect of cross section shape in heat transfer from a Fin.
- Heat transfer from Fins of two different materials.
Additional practical possibilities:
- Measuring the temperature distribution along an extended surface.
Practices to be done with the Unsteady State Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/EIB):
- Predicting temperature at the center of a cylinder using transient conduction with convection.
- Predicting the conductivity of a similar shape constructed from a different material.
- Conductivity and temperature dependence on volume.
- Conductivity and temperature dependence on surrounding temperature T∞.
Practices to be done with the Thermal Conductivity of Liquids and Gases Unit for TSTCB (TXC/LGB):
- Determining the heat losses of the system.
- Obtaining the thermal conductivity of gases and liquids.
- Thermal conductivity under vacuum conditions.
- Determining the temperature distribution in cylindrical bodies.
Additional practical possibilities:
- Obtaining of the curve of thermal conductivity of the air.
- Water thermal conductivity determination.
- Thermal conductivity determination of a mineral oil.
- Calibration of the unit.
- Dry air thermal conductivity under atmospheric pressure.
Practices to be done with the Free and Forced Convection Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/FFB):
- Free convection in flat surfaces.
- Forced convection in flat surfaces.
- Efficiency calculation of the forced convection process in flat plate.
- Forced convection in a pinned exchanger: efficiency.
- Forced convection in a finned exchanger: efficiency.
- Temperature distribution in the additional surfaces.
Additional practical possibilities:
- Demonstration of the basic principles of free and forced convection.
- Comparison between free and forced convection.
- Dependence of the heat transfer with the temperature.
- Dependence of the heat transfer with the speed of the fluid.
- Dependence of the heat transfer with the exchanger geometry (finned or pinned surface).
- Study of the advantage of using pinned and finned surfaces in heat transfer in free convection.
- Study of the advantage of using pinned and finned surfaces in heat transfer in forced convection.
- Comparative study between the free convection of a horizontal surface and vertical surface.
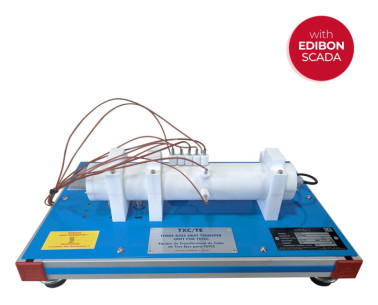
Practices to be done with the Three Axes Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/TEB):
- Conduction in a simple bar.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity of "K".
Additional practical possibilities:
- Conduction through three axes.
Practices to be done with the Metal to Metal Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/MMB):
- Conduction in a simple bar.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity of "k".
- Determination of the thermal contact resistance Rtc.
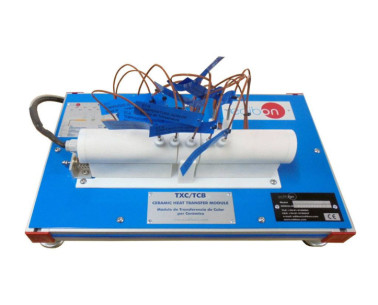
Practices to be done with the Ceramic Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/TCB):
- Conduction in a simple bar.
- Determination of the thermal conductivity "k".
- Conduction through a compound bar.
- Determination of the thermal contact resistance Rtc.
Practices to be done with the Insulating Material Heat Transfer Unit for TSTCB (TXC/TIB):
- Determination of the thermal conductivity "k".
- Calculation of the heat transfer properties of different specimens.
- Conduction through a compound bar.
- Insulation effect.
 Настройки cookie
Настройки cookie