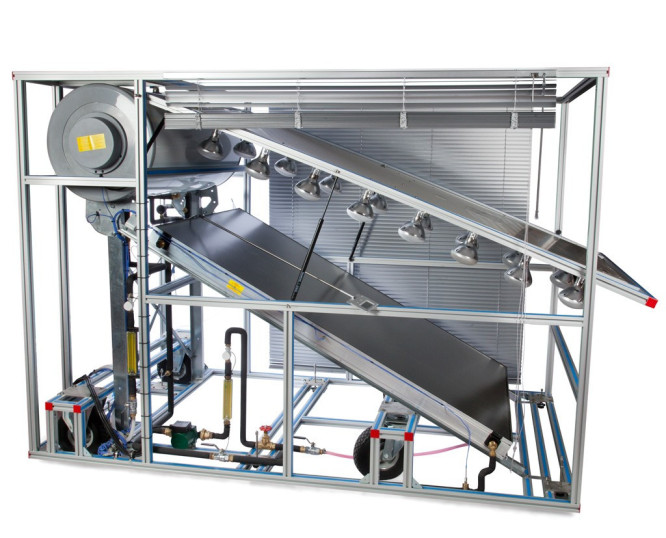
For decades, the traditional energy model has relied on large, centralized power plants that generate electricity and distribute it through extensive grids to end users. While this model has proven effective, it now faces major challenges: the need to integrate intermittent renewable energy...
At EDIBON, we reaffirm our commitment to the advancement of clean and renewable energy, with a special focus on green hydrogen as a key driver for a more sustainable future. We are proud to have been selected to equip the first Green Hydrogen Laboratory in the Region of Murcia, a pioneering space...
The shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) has gained considerable momentum worldwide, promising a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a path to a more sustainable future. However, as the demand for EVs accelerates, so too does the need for large quantities of essential minerals, such as...
At EDIBON, we are committed to strengthening skills as a strategic pillar for the competitiveness and social well-being of the European Union. Proper training not only boosts the economy but also enables individuals to fully participate in society and democracy.
 Preferensi cookie
Preferensi cookie