The KNX Automation Installations in Buildings Application, "AEL-KNX", designed by EDIBON, provides students, teachers and automation professionals with a unique opportunity to enter the world of KNX building automation project development, interconnection of KNX devices and programming with the ETS software tool. From basic electrical connections to advanced programming, users trained with this application will gain crucial practical and theoretical skills for project design and maintenance of automation systems.
The relevance of KNX in building automation is undeniable. For this reason, using the "AEL-KNX" application, it will be possible to carry out from the precise control of lighting, air conditioning, security, shutter control, etc. to the complete management of buildings through a Building Management System (BMS).
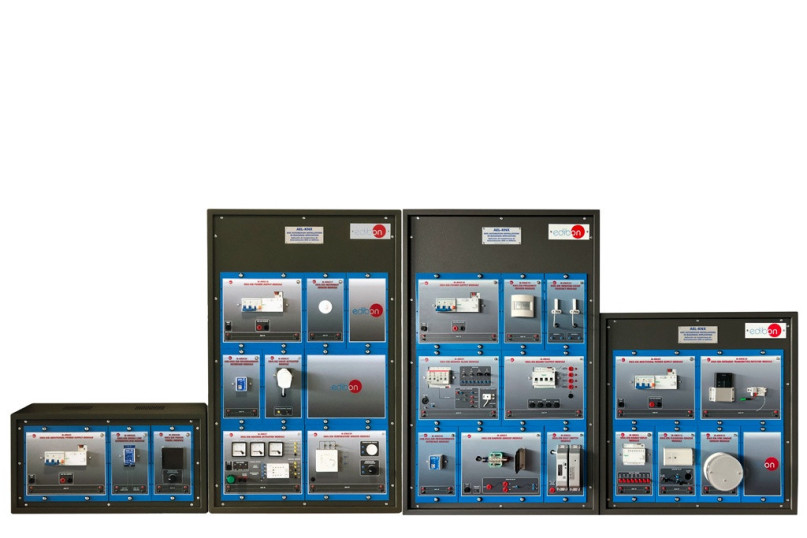
We have multiple KNX modules strategically grouped together to study the different solutions that are applied in real automation installations. For this reason, various configurations are recommended based on technical and teaching requirements. The minimum supply consists of two main elements: the AEL-KNX Base Unit, "AEL-KNX-UB," and at least one of the required elements of the AEL-KNX Base Unit, "AEL-KNX-UB."
The AEL-KNX Base Unit, "AEL-KNX-UB," includes the following elements:
- N-KNX34. USB KNX/EIB Programming Interface Module.
- N-KNX18. KNX/EIB Power Supply Module.
- N-KNX4. KNX/EIB Binary Input Module.
- N-KNX5. KNX/EIB Binary Output Module. (2 units).
- N-KNX30. KNX/EIB Touch Panel Module.
- N-KNX35. KNX/EIB Infrared Transmitter/Receiver Module.
- MED65. Digital Multimeter.
Required elements of the AEL-KNX Base Unit, "AEl-KNX-UB" (at least one) (Not included):
- AEL-KNX-LIC. KNX Lighting Control Training Application. Study of programming and lighting control, management of communication gateways for DALI lighting control.
- This application is designed to facilitate the study and understanding of KNX wiring practices specifically tailored for lighting control systems. This application serves as a valuable tool for educational and professional purposes, providing hands-on experience and knowledge of the wiring, programming and commissioning techniques associated with KNX technology in the context of lighting control applications. Direct dimming via lighting sensors and push buttons, use of KNX/DALI gateways for the integration of this technology in KNX lighting projects.
- AEL-KNX-HVAC. KNX for HVAC Control Training Application. Study of the programming and efficient management of HVAC systems. The importance of the correct parameterization of various air conditioning controllers.
- This application is designed to facilitate the study and understanding of KNX-based Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC) control systems. This application serves as a valuable tool for educational and professional purposes, providing hands-on experience and knowledge of the wiring, programming and commissioning techniques associated with KNX technology in the context of HVAC applications.
- AEL-KNX-BC. KNX Blind Control Training Application. Implementation of strategies to optimize the use of natural light, scene programming, etc.
- This application is designed to facilitate the study and understanding of KNX based blind control systems. This application serves as a valuable resource for educational and professional purposes, providing hands-on experience and knowledge of the wiring, programming and commissioning techniques associated with KNX technology in the context of blind control systems.
- AEL-KNX-SFC. KNX Security Control Training Application: Fire, Anti-intrusion, Floods, etc. Practices involving the use of detectors to ensure building security. Anti-intruder alarms, fire alarms, flood alarms, etc.
- This application is designed to provide hands-on experience and knowledge of KNX wiring practices specific to security systems. This application is designed for educational and professional purposes, allowing users to study and understand the wiring, programming and commissioning techniques associated with the integration of KNX technology in security related applications.
- AEL-KNX-BMS. Building Control Training Application via BMS. Allows the exploration of how KNX contributes to integrated building management. This set of devices are essential in large systems where visualization and management of system variables is essential.
- This application is designed to provide knowledge and experience in KNX programming practices specifically tailored for building management systems (BMS). This application serves as a valuable resource for educational and professional institutions and training centers focused on building automation, allowing students to understand the complexities of KNX device wiring, programming and commissioning in the context of BMS applications.
The "AEL-KNX" application includes a manual that serves as a learning guide for a correct installation of the KNX devices. In addition, it explains step by step how to wire the devices and how to program them according to their task. All KNX programming exercises are based on the standard ETS programming software.
This training application offers a complete immersion into the world of KNX, preparing students, engineers and industry professionals for practical challenges in the field of building automation.
 Настройки cookie
Настройки cookie